Abstract
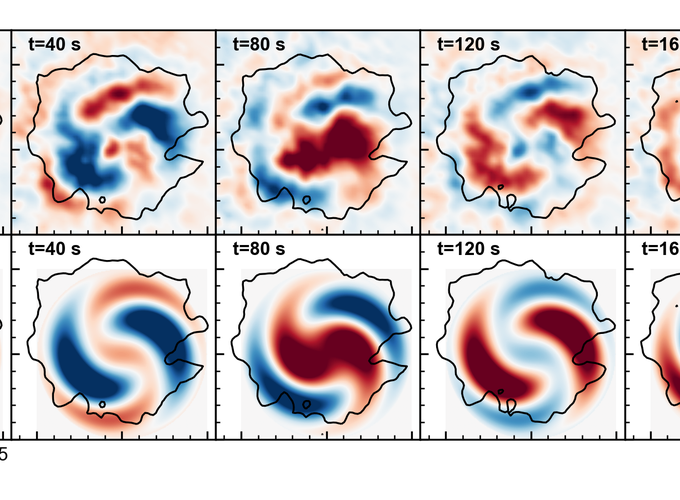
Recently, spiral wave patterns (SWPs) have been detected in 3 minute oscillations of sunspot umbrae, but the nature of this phenomenon has remained elusive. We present a theoretical model that interprets the observed SWPs as the superposition of two different azimuthal modes of slow magnetoacoustic waves driven below the surface in an untwisted and non-rotating magnetic cylinder. We apply this model to SWPs of the line-of-sight (LOS) velocity in a pore observed by the Fast Imaging Solar Spectrograph installed at the 1.6 m Goode Solar Telescope. One- and two-armed SWPs were identified in instantaneous amplitudes of LOS Doppler velocity maps of 3 minute oscillations. The associated oscillation periods are about 160 s, and the durations are about 5 minutes. In our theoretical model, the observed spiral structures are explained by the superposition of non-zero azimuthal modes driven 1600 km below the photosphere in the pore. The one-armed SWP is produced by the slow-body sausage (m = 0) and kink (m = 1) modes, and the two-armed SWP is formed by the slow-body sausage (m = 0) and fluting (m = 2) modes of the magnetic flux tube forming the pore.